
by Matthew G. Naugle
Wiley Computer Publishing, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ISBN: 0471196568 Pub Date: 11/01/98

|
Illustrated TCP/IP
by Matthew G. Naugle Wiley Computer Publishing, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN: 0471196568 Pub Date: 11/01/98 |
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
This protocol is used when a network station knows its MAC address but does not know its IP address. When would this happen? Diskless workstations are a good example. Notice that RARP uses the ARP packet format and does not involve IP; therefore, this packet cannot be routed. This protocol has been in use for some time, but there are other protocols that do a better job. This is one of the reasons that we use BOOTP and DHCP for address assignment because they can be forwarded over a router (with a little assistance from the router). One problem with RARP is that like its cousin ARP, it does not use IP. Therefore, RARP is generally used only on a LAN.
The requesting client machine will send out a RARP request to a server located on the local segment that has the RARP server service running on it. This RARP server will respond to the request with that particular station’s IP address. Although the RARP server does not need to be located on the same cable segment or extended LAN, it is preferred. Some router vendors have enabled their routers to forward these requests and responses to other networks.
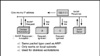
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
The packet format for a RARP packet is the same as for ARP. The only difference is that the field that will be filled in will be the sender’s physical address. The IP address fields will be empty. A RARP server will receive this packet, fill in the IP address fields, and reply to the sender—the opposite of the ARP process.
Other protocol similar to this are BOOTP and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). DHCP is more powerful than RARP, but it does supply one of the same functions as RARP: resolving an IP address. Besides being less functional than DHCP, RARP only works on single subnets. RARP works at the datalink layer and therefore cannot span subnets gracefully. DHCP can span subnets.
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |