
by Matthew G. Naugle
Wiley Computer Publishing, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ISBN: 0471196568 Pub Date: 11/01/98

|
Illustrated TCP/IP
by Matthew G. Naugle Wiley Computer Publishing, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN: 0471196568 Pub Date: 11/01/98 |
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
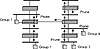
Some multicast forwarding algorithms, such as DVMRP, broadcast (floods) the first packet that it receives and then waits for Prune messages from the downstream interfaces. The Prune messages come back from multicast routers in response to receiving unwanted multicast traffic at the leaves of the multicast tree; therefore, finding the leaf networks for any multicast tree is important. These routers that connect to leaf networks start the pruning process by identifying which downstream interfaces do not belong to the multicast group. Routers that identify these interfaces prune those interfaces. If after pruning its own interfaces, the router finds that none of its interfaces belong to that group, it will send a Prune message upstream to its neighbor. If the router continues to receive multicast datagrams for that source, it will continue to send Prune messages (increasing the delta between them) until the multicast traffic for that group stops.
A prune lifetime is about two hours.
To join new receivers back onto the tree, the Graft message is sent. This message is sent hop by hop to each multicast router. Each message is acknowledged between routers to ensure that it was received, thereby guaranteeing end-to-end delivery. Routers that receive Graft messages can make a series of decisions.
If the receiving router has a prune state for the (source, group) pair, then it acknowledges the Graft message and sends a Graft message of its own to its upstream router. If the router has some pruned downstream interfaces but not a pruned upstream interface, it simply adds that interface to the list of downstream interfaces in its routing table. It will also send an acknowledgment to the source of the Graft message. If the router has no state (pruned or otherwise) for the (source, group) pair, then any received datagrams for the (source, group) pair should be automatically flooded. A graft acknowledgment is sent to the source of the Graft message as well.
Pruning and Grafting (Definition)
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |